Getting Started
Customizing the Layout
Main Toolbar Buttons
File Toolbar
These buttons allow you to load image files and save projects:

This group of buttons allows you to open and create new workspaces and opens the Import project dialog:

View Settings Toolbar
This button allows you to switch to the Data Management layout, a predefined view setting that opens the workspace and view settings window.

This button allows you to open the View Settings dialog. Add layers via drag and drop and edit image, vector and point cloud view settings. Additionally, select image view options, offering views of layers, classifications and any features you wish to visualize.

Zoom and Navigate Toolbar
This region of the toolbar offers direct selection and the ability to drag an image, along with several zoom options and allows you to select maps.
View Settings dialog
Overview
eCognition offers the possibility to add all kinds of data via drag and drop to the View Settings dialog. You can add image layers, vector and point cloud layers to a new or existing project. Select the layers in the Windows File Explorer and drag and drop them to the View Settings dialog to import them. The upper pane allows individual layer settings, the lower pane global view settings for the respective data type. (Alternatively, you can select File > Add data layer or View > Source View > Add data layer button). Furthermore, eCognition project (.dpr) and workspace (.dpj) files can be added to eCognition by drag and drop.
 This button toggles between an expanded or collapsed view of layers, visualizing or leaving out details of loaded layers.
This button toggles between an expanded or collapsed view of layers, visualizing or leaving out details of loaded layers.
These buttons toggle the file diplay and visualize different image layers in grayscale or in RGB. If more than one image layer is loaded, they also allow to shift between layers and their layer mixing (details see below).
The 3D button opens the 3D toolbar (active on availability of at least one point cloud layer).
Image layer buttons
 Single Layer Grayscale
Single Layer Grayscale
Scenes are automatically assigned RGB (red, green and blue) colors by default when image data with three or more image layers is loaded. Use the Single Layer Grayscale button in the View Settings dialog to display image layers separately in grayscale. To change from RGB to grayscale mode, press the button and the first image layer is shown in grayscale mode. Step through all loaded image layers by using the Show Next/Previous Image Layer button or open multiple views for comparison.

 Three Layers RGB
Three Layers RGB
This button displays the first three layers of your scene in RGB. By default, layer one is assigned to the red channel, layer two to green, and layer three to blue indicated by a small circle in the respective field. View settings can be changed by single click on a circle (removes circle) or an empty field (adds circle).
 Show Previous Image Layer
Show Previous Image Layer
In Grayscale mode, this button displays the previous image layer. The number or name of the displayed image layer is indicated in the middle of the status bar at the bottom of the main window.
In Three Layer Mix, the color composition for the image layers changes one image layer up for each image layer. For example, if layers two, three and four are displayed, the Show Previous Image Layer Button changes the display to layers one, two and three. If the first image layer is reached, the previous image layer starts again with the last image layer.
 Show Next Image Layer
Show Next Image Layer
In Grayscale mode, this button displays the next image layer down. In Three Layer Mix, the color composition for the image layers changes one image layer down for each layer. For example, if layers two, three and four are displayed, the Show Next Image Layer Button changes the display to layers three, four and five. If the last image layer is reached, the next image layer begins again with image layer one.
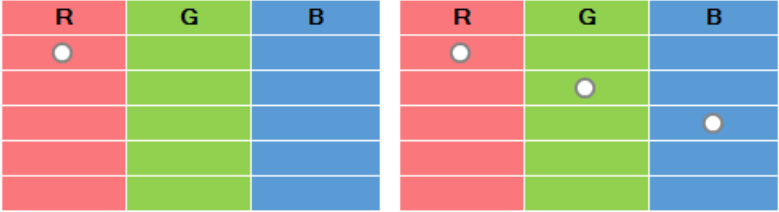
Image Layer Properties and Settings
Upper pane - Individual Image Layer Properties
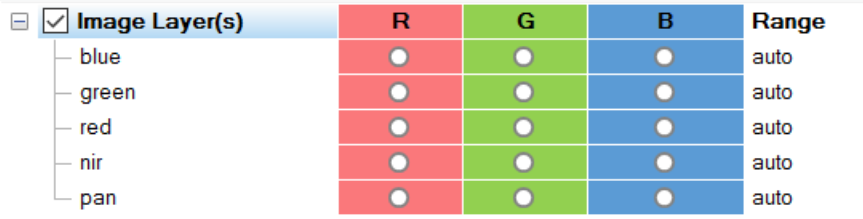
R-G-B: To define the display color of each image layer, you can add a circle for the red, green and blue channels by single click for each layer separately. They are then displayed as additive colors in the view. Any layer without a circle in at least one column is not shown. When creating a new project, the first three image layers are displayed in red, green and blue.
A right-click on the image layers opens the context menu where you can select to Show All or Hide All image layers at once.
One layer can be displayed in more than one color, and more than one layer can be displayed in the same color. Change these settings to your preferred by clicking in the respective R, G or B cell.
Range: For the equalization settings (lower pane of dialog) manual, false color (hot metal) and false color (rainbow), you can define the displayed range individually based on the Image Layer Equalization dialog for each image layer. To open the dialog click on the small dots at the end of the line of the image layer you want to adjust (details see Equalization and Image Layer Equalization dialog.)
Changing the view settings only changes the visual display of the image but not the underlying image data – it has no impact on the process of image analysis. You can define the color composition for the visualization of image layers in the view. Additionally, you can choose from different equalizing options. This enables you to better visualize the image and to recognize the visual structures without actually changing them. You can also choose to hide layers, which can be very helpful when investigating image data and results.
Lower pane - Global Image Layer Settings
By changing the Global Settings in the lower pane - all settings in the upper pane are overwritten.
Background: Click on the square to change the background color of the image view.
Raster mode: Select between Image Data and samples (rasterized). If vector layers or a samples in a TTA mask are loaded the view visualizes a rasterized version of these layers. (The rasterized layer is used in segmentation algorithms.)
Equalization: There are several modes for image equalization stretches. Compare the available methods and choose one that gives you the best visualization of the objects of interest. Equalization settings are stored in the workspace and applied to all projects within the workspace, or are stored within a separate project. In the Options dialog box you can define a default equalization setting. Select on of the following modes:
- none: No equalization allows you to see the scene as it is, which can be helpful at the beginning of rule set development when looking for an approach. The image layer is displayed without further modification.
- linear: Linear equalization with selectable saturation factor [Range 0-50]. Default value 1.00%. Displays images with a higher contrast than without image equalization.
- standard deviation: This equalization has a default factor of 3.0 and renders a display similar to the linear equalization. Use a parameter around 1.0 for an exclusion of dark and bright outliers [Range 0-10].
- gamma correction: Equalization used to improve the contrast of dark or bright areas by spreading the corresponding gray values [Range 0-5]. Default factor 0.5.
- histogram: The histogram equalization increases the contrast of image layer but can lead to over-stretching. Because intensity values are better distributed on the histogram, it can be helpful in cases where you want to display areas with more contrast.
- manual: Image Layer Equalization enables you to control equalization in detail for each layer individually.
Select either the Range field in the upper pane of the dialog and insert border values to be displayed. Alternatively you can open the Image Layer Equalization dialog by single click on the small dots at the end of the column. For details see also Image Layer Equalization dialog. - false color (hot metal): is recommended for single image layers with large intensity ranges to display in a color range from black over red to white.
Select either the Range field in the upper pane of the dialog and insert border values to be displayed. Alternatively you can open the Image Layer Equalization dialog by single click on the small dots at the end of the column. For details see also Image Layer Equalization dialog. - false color (rainbow): is recommended for single image layers to display a visualization in rainbow colors. Here, the regular color range is converted to a color range between blue for darker pixel intensity values and red for brighter pixel intensity values.
Select either the Range field in the upper pane of the dialog and insert border values to be displayed. Alternatively you can open the Image Layer Equalization dialog by single click on the small dots at the end of the column. For details see also Image Layer Equalization dialog.
Auto update: This checkbox updates the view with each change of the view settings on the fly. Clear this check box to show the new settings after clicking Apply only. With the Auto update check box cleared, the Discard and Apply buttons become active.
Apply to all views: With this checkbox activated you can apply selected settings to all views at once.
The order of image layers and their aliases can be changed easily in the Source View dialog (View > Source View).
Image Layer Equalization dialog
To open the Image Layer Equalization dialog, single click on the small dots at the end of the line of the image layer you want to adjust. In this dialog you can define the input range by either setting minimum and maximum values, or dragging the borders with the mouse (yellow lines). The equalization range can be set for each layer individually.
It is also possible to adjust these parameters for all image layers using the mouse with the right-hand mouse button held down in the image view: moving the mouse horizontally adjusts the center value; moving it vertically adjusts the width of the interval. (This function must be enabled in: Tools > Options > Display > Use right-mouse button for adjusting window leveling > Yes).
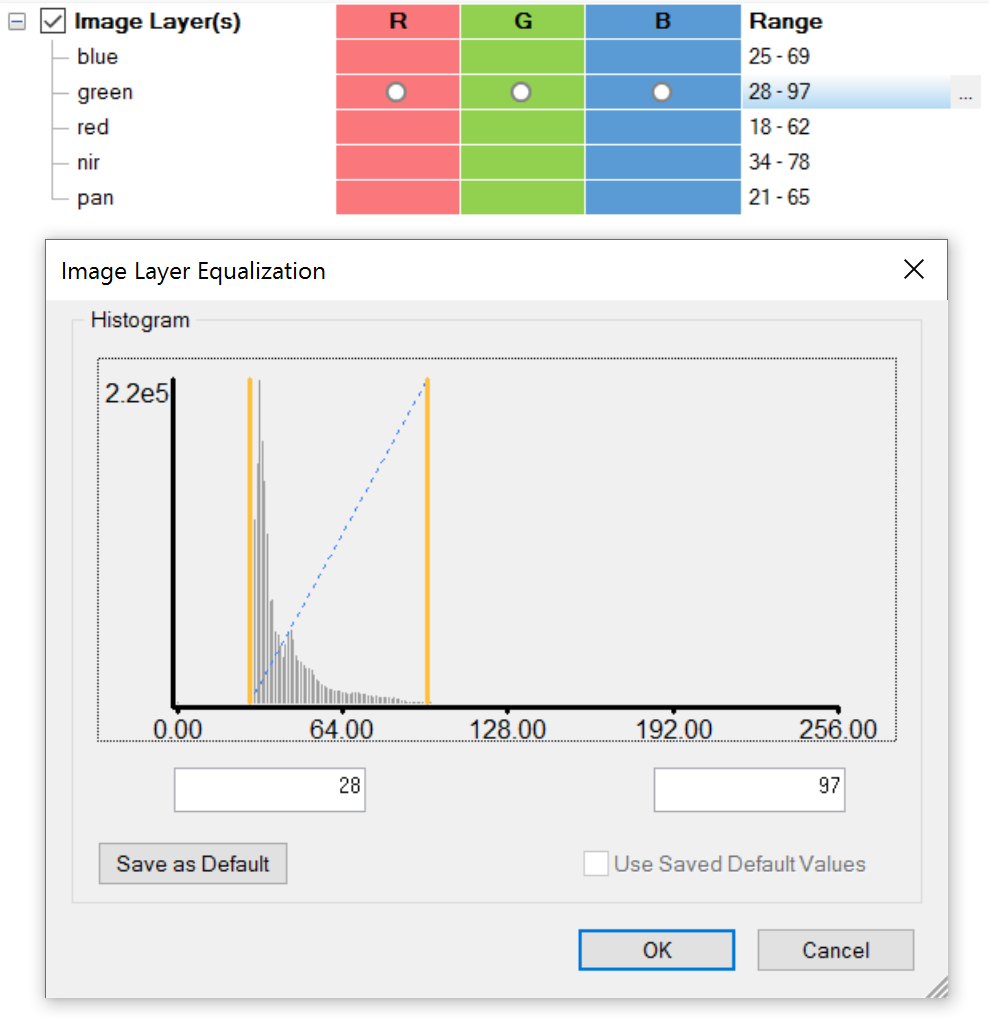
Image equalization is performed after all image layers are mixed into a raw RGB (red, green, blue) image. If, as is usual, one image layer is assigned to each color, the effect is the same as applying equalization to the individual raw layer gray value images. On the other hand, if more than one image layer is assigned to one screen color (red, green or blue), image equalization leads to higher quality results if it is performed after all image layers are mixed into a raw RGB image.
Ignore Range: Activating the Ignore range check-box you can enter a range of values that will be ignored when computing the image statistics for the image equalization. (Only active for Equalizing modes linear, standard deviation, gamma correction and histogram)
This option is useful when displaying e.g. elevation data excluding values and background areas in visualization.
This option is only for image visualization. No data values can also be assigned when creating a project see chapter Assigning No-Data Values in Projects and Workspaces.
Point cloud properties
The point cloud settings can be changed in the upper and lower pane of the View Settings dialog. Point cloud layers can be shown individually using the respective checkbox of a single point cloud layer. Deactivate the Point Clouds checkbox to hide all point cloud layers in the view or select specific point clouds to hide. You can change the order of point cloud layers by drag and drop within the Point Clouds section.
For details see also User Guide > Projects and Workspaces > Working with Point Clouds.
3D toolbar button : This button is active on availability once a point cloud layer is loaded to the project. Open this toolbar to select a subset using one of the 3D subset selection buttons and for more visualization options. Subsequently, an additional window is opened where the subset is visualized in 3D (for further details see Navigating in 3D). You can shift the subset when the left view is active, using the left, right, up and down arrows of your keyboard.
With the 3D viewer active, image layers can be activated in the View Settings dialog (upper pane) and are then visualized as a 2D image in the 3D viewer. The default elevation for the image layer is the minimum elevation of all currently displayed point cloud points in the 3D viewer (-auto-). Change the elevation of the image layer by using the parameter in the lower pane Elevation (3D view) and enter a new height value (in project unit).
3D vector layers can be displayed in the 3D viewer, supporting 2D and 3D points, lines and polygon outlines (without fill).
The Zoom Scene to Window button  helps you to reset the observer position, all zoom and rotation steps to default.
helps you to reset the observer position, all zoom and rotation steps to default.
With point cloud data loaded you can open the toolbar also via View > Toolbars > 3D.
Upper pane of View Settings dialog - Point Cloud Properties
Mode: Choose the visualization mode (see lower pane).
Point Size: Choose the point size in a range between 1 (small) to 10 (large).
Fixed Color: View all points in one selectable color. Only active for Render mode Fixed color.
Lower pane - Point Clouds Global Settings
By changing the Global Settings in this lower pane - all settings in the upper pane are overwritten.
Background: Click on the square to change the background color of the image view. E.g. for the intensity render mode you achieve an improved visualization if you select background color white.
Render mode: Choose the visualization mode:
- Fixed color - view all points in one selectable color
- Classification - one selectable color per LAS-class (optional layer)
- Intensity - gray scale visualization of intensity layer
- Color-coded intensity - gray to red visualization of intensity layer
- RGB - view points colored based on RGB image (optional layer)
- Height - view points colored by elevation (color gradient blue (low) - green - red (high))
The same Render Mode is applied to all point cloud layers and cannot be chosen individually for each point cloud file. However, with the check-box Apply to all views inactive - different point cloud view settings can be chosen for the respective active window (e.g. left window height & right window classification).
Point Size: Choose the point size in a range between 1 (small) to 10 (large).
Available Classes: If your point cloud data contains LAS-classes you can switch each class on and off individually. In Render mode > Classification you can change the default color for a class by click on the colored rectangle.
Auto update: This checkbox updates the view with each change of the view settings on the fly. Clear this check box to show the new settings after clicking Apply only. With the Auto update check box cleared, the Discard and Apply buttons become active.
Apply to all views: Activate this checkbox to apply the settings to both views.
Vector Layer Display
The vector layer settings can be changed in the upper pane (individual vector layer settings) and lower pane (global settings) of the View Settings dialog. You can change the order of thematic layers by drag and drop.
All thematic layers can be activated and inactivated for display via the Vector Layers checkbox, or individually using the respective checkbox of a single vector layer.
Upper pane - Individual Vector Layer Properties
Outline: Select an outline color for vector layers.
Fill: Choose a fill color for polygons.
Outline width: The value for the outline width changes the thickness of the vector outline for all vector layers. (This value is saved in the user settings and therefore applied to different projects.)
Transparency: Select the transparency for a vector layer individually.
Lower pane - Vector Layers Global Settings
By changing the Global Settings in this lower pane - all settings in the upper pane are overwritten.
Background: Click on the square to change the background color of the image view.
Outline width: The value for the outline width in this lower pane of the dialog changes the thickness of the vector outline for all vector layers. (This value is saved in the user settings and therefore applied to different projects.)
Auto update: This checkbox updates the view with each change of the view settings on the fly. Clear this check box to show the new settings after clicking Apply only. With the Auto update check box cleared, the Discard and Apply buttons become active.
Apply to all views: With this checkbox activated you can apply selected settings to all views at once.
Splitting Windows
There are several ways to customize the layout in eCognition Developer, allowing you to display different views of the same image. For example, you may wish to compare the results of a segmentation alongside the original image.
Selecting Window > Split allows you to split the window into four – horizontally and vertically – to a size of your choosing. Alternatively, you can select Window > Split Horizontally or Window > Split Vertically to split the window into two.
There are two more options that give you the choice of synchronizing the displays. Independent View allows you to make changes to the size and position of individual windows – such as zooming or dragging images – without affecting other windows. Alternatively, selecting Side-by-Side View will apply any changes made in one window to any other windows.
A final option, Swipe View, displays the entire image into across multiple sections, while still allowing you to change the view of an individual section.
Docking
By default, the four commonly used windows – Process Tree, Class Hierarchy, Image Object Information and Feature View – are displayed on the right-hand side of the workspace, in the default Develop Rule Set view. The menu item Window > Enable Docking facilitates this feature.
When you deselect this item, the windows will display independently of each other, allowing you to position and resize them as you wish. This feature may be useful if you are working across multiple monitors. Another option to undock windows is to drag a window while pressing the Ctrl key.
You can restore the window layouts to their default positions by selecting View > Restore Default. Selecting View > Save Current View also allows you to save any changes to the workspace view you make.
eCognition Developer Views
View Layer
To view your original image pixels, you will need to click the View Layer button in the toolbar. Depending on the stage of your analysis, you may also need to select Pixel View (by clicking the Pixel View or Object Mean View button).
In the View Layer mode you can also switch between grayscale and RGB layers using the buttons in the View Settings dialog. To view an image in its original format (if it is RGB), you may need to press the Mix Three Layers RGB button .
![]()
View Classification
Used on its own, View Classification will overlay the colors assigned by the user when classifying image objects (these are the classes visible in the Class Hierarchy window) – the figure below shows the same image when displayed in pixel view with all its RGB layers, against its appearance when View Classification is selected.
Clicking the Pixel View or Object Mean View button toggles between an opaque overlay (in Object Mean View) and a semi-transparent overlay (in Pixel View). When in View Classification and Pixel View, a small button appears bottom left in the image window – clicking on this button will display a transparency slider, which allows you to customize the level of transparency.

Feature View
The Feature View button may be deactivated when you open a project. It becomes active after segmentation when you select a feature in the Feature View window by double-clicking on it.
Image or vector objects are displayed as grayscale according to the feature selected. Low feature values are darker, while high values are brighter. If an object is red, it has not been defined for the evaluation of the chosen feature.

Pixel View or Object Mean View
This button switches between Pixel View and Object Mean View.
Object Mean View creates an average color value of the pixels in each object, displaying everything as a solid color. If Classification View is active, the Pixel View is displayed semi-transparently through the classification. Again, you can customize the transparency in the same way as outlined in View Classification.
![]()
Show or Hide Outlines
The Show or Hide Outlines button allows you to display the borders of image objects that you have created by segmentation and classification. The outline colors vary depending on the active display mode:
- In View Layer mode the outline color is blue by default.
- In View Classification mode the outline color of unclassified image objects is black by default.
These two colors can be changed choosing View > Display Mode > Edit Highlight Colors.
- After a classification the outlines take on the colors of the respective classes in View Classification mode.

Image View or Project Pixel View
Image View or Project Pixel View is a more advanced feature, which allows the comparison of a downsampled scene (e.g. a scene copy with scale in a workspace or a coarser map within your project) with the original image resolution. Pressing this button toggles between the two views.
Navigating in 3D
If you have loaded point cloud data you can switch to a 3D visualization mode. The according 3D toolbar buttons are only active if point cloud data is loaded to your project.
Point Cloud Navigation and 3D Subset Selection
For adjustment of view settings see Point Cloud View Settings.
Once you have selected 3D data to be shown in the View Settings dialog you have to choose a 3D subset: Activate the 3D toolbar ![]() and draw a rectangle in the view using the subset button
and draw a rectangle in the view using the subset button  . A new window is opened (right window) where the selected region is visualized in 3D.
. A new window is opened (right window) where the selected region is visualized in 3D.
Alternatively, you can define a rectangle that lies in the view non-parallel to the window: Open the 3D toolbar (View > Toolbars > 3D) and select the 3 click 3D subset selection button. This is helpful e.g. for selection of items in the view that are not parallel to the window or for corridor mapping data sets (see 3D Predefined View).
You can shift a selected subset using the left, right, up and down arrows of your keyboard with the left view active.
The 3 D subset selection can only be applied if one single window is opened on your screen.
If you are already in 3D mode and split the main window horizontally, the 3D mode is inactivated.
In the main window (left) a small arrow appears that shows the current observer position.
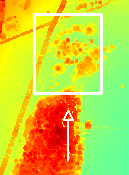
In the 3D window (right) the following control scheme is applied:
- Left Mouse Button (LMB): While holding down the LMB you can move the mouse up (zoom out) and down (zoom in) to achieve a smooth zooming. This zooming corresponds directly to mouse movement. The cursor turns to a double-pointed arrow.
- Left Mouse Button (LMB): With the Image Object Information window open and point cloud features selected in the Feature view - a single click on a point cloud point shows feature values for the selected point that is visualized as a big red dot. (To change the color go to View > Display mode > Edit highlight colors > Selection color.) When you select a point in the 3D view the same point is highlighted in the main window and vice-versa.
- Right Mouse Button (RMB): While holding down, RMB is used for rotating the point cloud around a center point located in the middle of the selected subset. The cursor turns to a circular arrow and the center point of the subset appears.
Right Mouse Button (RMB) - with activated custom center of rotation : While holding down, RMB is used for rotating the point cloud, now with the center of rotation located at the position where this right mouse button was activated.
: While holding down, RMB is used for rotating the point cloud, now with the center of rotation located at the position where this right mouse button was activated. - Mouse Wheel: Rotating the wheel produces a discrete zoom. This zooming is performed in individual steps, corresponding to the rotation of the wheel. The cursor turns to a double-pointed arrow.
- Both LMB and RMB / Press Mouse Wheel: Holding down both the left and right mouse buttons or pressing the mouse wheel enables the user to pan in 3D space. The cursor turns to a hand.
- Alternatively, from the toolbar you can also select the Panning button or the Zoom Out Center and Zoom In Center buttons.
 Zoom Scene to Window button: helps you to reset the observer position, all zoom and rotation steps to default.
Zoom Scene to Window button: helps you to reset the observer position, all zoom and rotation steps to default.
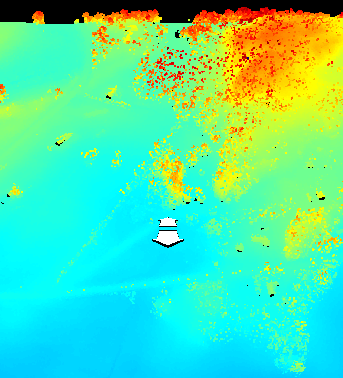
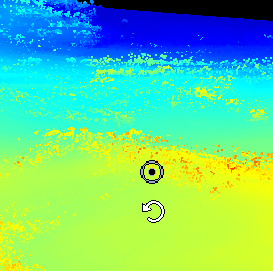
3D Predefined View
With 3D data loaded an additional toolbar for predefined settings can be opened via
View > Toolbars > 3D:
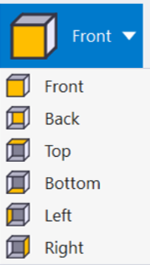
To select a predefined 3D view, choose one of the drop-down commands:
Front, Back, Top, Bottom, Left or Right.
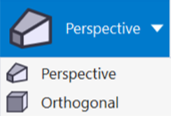
To toggle between different 3D projections, select either
- Perspective - parallel projected lines appear to converge as they recede in the view or
- Orthogonal - parallel projected lines appear to remain parallel as they recede in the view
The 3 click 3D subset selection button  lets you define a rectangle by three clicks that can lie in the view non-parallel to the window. This is helpful e.g. for selection of items in the view that are not parallel to the window or for corridor mapping data sets. You can shift the subset using the left, right, up and down arrows of your keyboard with the left view active.
lets you define a rectangle by three clicks that can lie in the view non-parallel to the window. This is helpful e.g. for selection of items in the view that are not parallel to the window or for corridor mapping data sets. You can shift the subset using the left, right, up and down arrows of your keyboard with the left view active.
Activating the Custom center of 3D rotation button  : While holding down the Right Mouse Button (RMB) for rotating the point cloud, the center of rotation is located at the position where this right mouse button was activated.
: While holding down the Right Mouse Button (RMB) for rotating the point cloud, the center of rotation is located at the position where this right mouse button was activated.
Time Series
The map features of eCognition also let you investigate time series data sets - which corresponds to a continuous film image.
There are several options for viewing and analyzing image data represented by eCognition maps. You can view time series data using special visualization tools.
3D Toolbar - Time Series

Go to View > Toolbars > Time Series to open the toolbar for the following functionality:
- Navigation: Use this slider to navigate through the frames of a video (time series)
- Start/Stop Animation: Start and stop animation of a video (time series)
- Show Next Time Frame: Display next time frame in the planar projections
- Show Previous Time Frame: Display next time frame in the planar projections
Viewing a Video (Time Series)
Image data that includes a video (time series) can be viewed as an animation. You can also step though frames one at a time. The current frame number is displayed in the bottom right corner of the map view.
To view an animation of an open project, click the play button in the Animation toolbar; to stop, click again. You can use the slider in the Animation toolbar to move back and forth through frames. Either drag the slider or click it and then use the arrow keys on your keyboard to step through the frames. You can also use buttons in the 3D Settings toolbar to step back and forth through frames.

